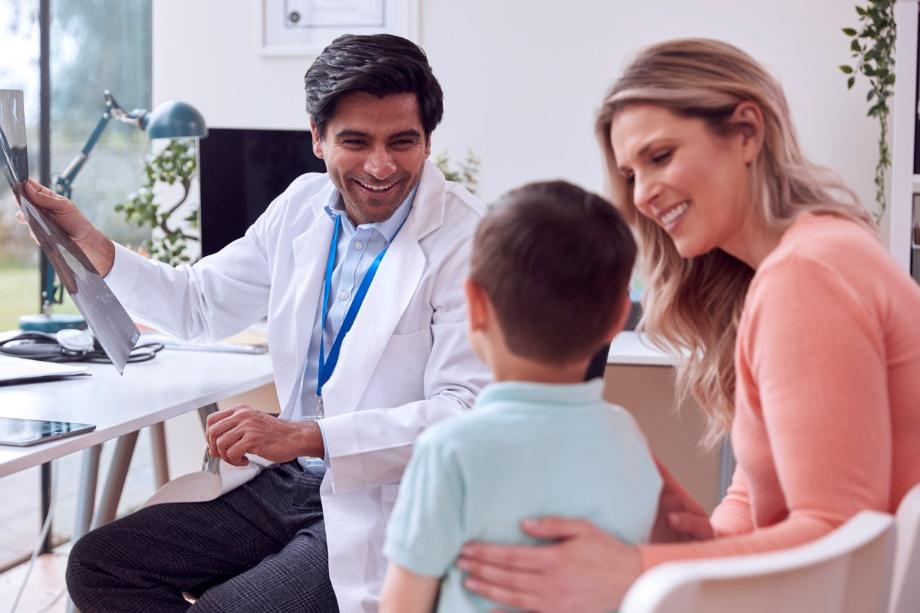
Family nurse practitioners (FNPs) are advanced practice nurses specializing in family-focused healthcare. FNPs undergo extensive training and education, developing expertise in diagnosing, treating and managing health conditions. As holistic providers, they consider physical and emotional wellbeing, as well as social factors when providing holistic services.
They play many roles within healthcare, as primary care providers, health promotion advocates, chronic disease management specialists, research contributors and educators. FNPs serve as comprehensive, frontline care while simultaneously championing disease prevention by educating patients and communities alike. FNPs manage chronic conditions by supporting patients throughout their healthcare journey while shaping future healthcare practices through research and policy development initiatives and acting as educators guiding aspiring healthcare professionals.
Primary care providers
Family nurse practitioners serve as vital primary care providers, filling gaps in healthcare where access may be limited and contributing to its sustainability by diagnosing, treating and managing health conditions. They play a critical role in supporting our healthcare system.
Role of FNPs in primary care
Family nurse practitioners hold a special place within healthcare. Often seen as being at the core of modern health services, FNPs provide unique patient care perspectives that distinguish them. FNPs embrace an approach emphasizing holistic wellbeing, which extends far beyond treating diseases or immediate health concerns. They emphasize their patients’ overall wellness, stressing that health encompasses physical, mental and social wellbeing rather than simply an absence of illness.
This patient-centric approach enables healthcare practitioners to craft comprehensive treatment plans tailored to each patient’s lifestyle and health conditions, such as diet, exercise, stress levels and emotional wellbeing. Their emphasis on holistic wellness fosters active patient participation in managing health while creating an open partnership rather than directive relationships, which are critical ingredients in successful healthcare outcomes.
In addition, FNPs boast an expansive scope of practice that allows them to provide services to a diverse population, from infants to seniors. FNPs stand out among other nursing specialties as their extensive training enables them to offer comprehensive services throughout their patients’ lifespans. FNPs often work collaboratively with physicians as part of an effective healthcare team to deliver excellent patient care.
In many states, FNPs also possess autonomy over running their own clinics and providing primary care services independently. FNPs play an invaluable role in healthcare delivery, particularly in rural and underserved areas where physician access may be limited. Their unique position allows for direct patient care, ensuring comprehensive yet accessible healthcare solutions.
Responsibilities of FNPs as primary care providers
As primary care providers, FNPs provide comprehensive care to their patients. FNPs conduct routine checkups and screening tests; identify and manage chronic conditions such as hypertension, diabetes and heart disease; provide immediate treatment for minor injuries or illnesses as needed; advise patients on preventative health measures and healthy lifestyle choices; and serve as first point-of-contact for health system services.
In this role, FNPs perform an array of duties. From performing physical exams and ordering and interpreting tests to developing treatment plans and prescribing medications, FNPs play an integral role in healthcare provision. They also serve as patient advocates and intermediaries between various healthcare providers.
FNPs frequently work in underserved areas, providing care to individuals without easy access to healthcare services and helping bridge healthcare disparities.
They combine clinical expertise with knowledge about disease prevention and health promotion, making their role as primary care providers both pivotal and multidimensional. They ensure continuity of care while contributing significantly to public health.
Health promotion and disease prevention advocates
Promoting health and preventing disease are cornerstones of modern healthcare. As primary caregivers, family nurse practitioners champion these goals. They tirelessly promote healthier choices through their combination of medical knowledge and interpersonal abilities.
The role of FNPs in health promotion and disease prevention
FNPs play a multidimensional role in healthcare. One important facet is acting as health advocates; primary care specialists are well suited to influence patients’ healthcare choices and take an active approach towards disease prevention rather than simply treatment.
FNPs aim to encourage patients to adopt healthier lifestyles by emphasizing the value of balanced nutrition, physical activity and sufficient sleep — particularly highlighting these as critical aspects of wellbeing. They also discourage behaviors that are harmful to health, such as smoking and substance abuse. FNPs serve as beacons of information guiding individuals toward habits that enhance wellbeing.
FNPs also play a vital role in disease prevention. Through regular health screenings and early diagnosis, FNPs help detect potential health issues early on. This includes everything from chronic diseases such as diabetes and hypertension to life-threatening conditions such as cancer. Early detection increases the chances of successful management and treatment, making this role one of an FNP’s core duties.
Community education and intervention initiatives led by FNPs
Education is another primary tool in the FNPs’ health promotion and disease prevention toolkit. Backed by their conviction that knowledge leads to better decisions, FNPs educate communities alongside individual patients.
FNPs host educational workshops and seminars on various health-related topics. Workshops may focus on diabetes management or heart disease prevention; these initiatives help spread essential health knowledge, leading to healthier communities.
In addition, FNPs also lead targeted intervention programs designed to address health risks in specific community subsets. For example, an FNP may organize fitness programs specifically for elderly residents or tobacco cessation initiatives in high schools aimed at adolescents. These proactive interventions serve to stop health issues at their source.
Impact of FNPs on promoting healthier communities
The beneficial impacts of FNPs’ relentless efforts in health promotion and disease prevention reverberate throughout communities, cultivating healthier lifestyles while simultaneously creating environments that are conducive to good health.
Following advice from FNPs, individuals begin making more informed health decisions. They choose healthier meals, incorporate exercise into their routines and abandon harmful habits contributing to obesity or smoking-induced conditions. This leads to reduced prevalence rates.
FNPs’ educational and intervention initiatives have a noticeable ripple effect across communities. Through these types of initiatives, a broader cross-section of the population has come to understand preventive healthcare, seeking regular checkups and vaccinations at regular intervals. This results in earlier detection and management of health issues that lessen the overall burden on population health.
Overall, FNPs play an invaluable role in health promotion and disease prevention. From providing individual counseling and health education sessions to initiating community intervention initiatives, their efforts all reflect an ethos of advocacy, constantly working towards making their communities healthier places.
Chronic disease management specialists
Chronic diseases pose a substantial public health threat and require extensive management and attention from health providers, with family nurse practitioners playing an essential role in this regard.
Role of FNPs in managing chronic diseases
From diagnosis to treatment, FNPs provide comprehensive care encompassing every step in the journey: monitoring patients’ progress, adapting treatment plans as needed and assessing medication responses. They ensure effective control over chronic illnesses. For instance, when managing diabetes, FNPs monitor blood sugar levels and adjust insulin dosage. They may even advise diet changes to help manage it effectively and prevent complications that might otherwise arise from the condition.
FNPs and patient education on chronic disease management
Education is critical when managing chronic conditions. Patients need to understand their requirements, and FNPs play an essential role by providing necessary information about symptoms, complications and management methods for specific diseases. For instance, FNPs could teach someone with heart disease how to monitor their blood pressure at home while providing guidance about regular exercise and healthy diet habits. This helps to improve the patient’s decision-making capability and helps manage symptoms effectively.
Influence of FNPs on improving quality of life for chronic disease patients
FNPs play an incredible role in improving the quality of life for patients living with chronic diseases. Not only do they focus on managing the disease itself, but they also consider lifestyle, emotional health and social circumstances when providing advice about adapting to life with chronic disease. For instance, an FNP might suggest lifestyle adjustments for a person suffering from COPD, such as quitting smoking or installing air purifiers at home.
FNPs also provide emotional support. Chronic diseases can take an emotional toll, so regular visits with FNPs can make patients feel valued and understood while helping them manage the emotional aspects of their condition.
Different types of roles you can have as a family nurse practitioner
As a family nurse practitioner, there are various roles you may fill. One such position could involve working in a hospital setting, providing care to those suffering from chronic illnesses while focusing on disease management and acute care services. Your work could include educating patients and raising health awareness. You could become an essential player in preventing further healthcare needs.
In some cases, FNPs choose to specialize in certain areas. For instance, you could specialize in geriatrics as an FNP and focus your work on managing chronic diseases that commonly impact older adults. FNPs can also work in research or policymaking roles. Their knowledge can help shape health policies or explore potential treatments for chronic diseases.
In all these roles, FNPs are indispensable in managing chronic conditions. They offer care, education and enhanced quality-of-life to their patients. This makes the FNP role varied, rewarding and essential to today’s healthcare ecosystem.
Research and policy development contributors
Family nurse practitioners play many roles within healthcare. Not only do FNPs provide clinical care, but they are also integral parts of research and policy development teams. Let’s take a deeper dive into their roles within this sector:
FNPs in research: Contributions and case studies
In the field of research, FNPs are at the forefront of innovation when it comes to research. By collecting and analyzing patient data for trends in health and disease, FNPs often develop hypotheses that serve as foundations for more comprehensive medical studies. Through close relationships with patients, FNPs gain unique insights that are hard to replicate elsewhere.
In the case of obesity research, FNPs observing rising obesity rates among their patients could trigger studies that would examine lifestyle changes, diet plans or correlations between obesity and other medical conditions. This research could provide critical evidence-based findings to inform healthcare strategies moving forward.
Role of FNPs in health policy development and advocacy
FNPs play an invaluable role in health policy development. Their extensive experience working directly with patients and healthcare systems enables them to advise on policy modifications that improve patient care while making healthcare more accessible and efficient.
An FNP often advocates for improved nurse-to-patient ratios or modifications to prescription policies to make medications more cost-effective, constantly working alongside healthcare professionals and policymakers to champion reforms.
The impact of FNPs on policy changes and health outcomes
FNPs have a unique position as care providers and researchers that bridges the gap between theory and practice. They provide real-world input during policy debates to ensure practical policies that serve patients are implemented successfully.
An FNP’s involvement in policy change, such as increasing vaccination rates, can dramatically enhance community health outcomes, as their advocacy and educational efforts lead to more people getting immunized against disease spread and decreasing disease transmission rates.
Through their role in research and policy development, FNPs are integral contributors to broader healthcare environments. They serve as vital linchpins within the healthcare industry, driving change for patients’ wellbeing while supporting innovation.
Educators and mentors in nursing practice
Reputable institutions such as Texas Woman’s University (TWU) are pivotal in cultivating the skills needed to become a family nurse practitioner, an integral role in healthcare. Through programs such as those offered by TWU, there is a clear pathway demonstrating how to become family nurse practitioner which prepare students to make a difference in the healthcare field. Students have the opportunity to deepen their knowledge of advanced topics such as applied research, patient assessments, treatment methods and pharmacology. An online Master of Science – Family Nurse Practitioner degree provides the necessary training to deliver essential healthcare services and serve as an educator and mentor for nursing practices.
Role of FNPs in nursing education and mentorship
FNPs are well-recognized for their diverse roles in healthcare, offering a range of medical services. However, one should also acknowledge their vital contributions to education and mentorship as they- provide guidance and share their knowledge with aspiring nurses in an encouraging learning environment.
If you aim to become a family nurse practitioner, consider seeking guidance from one. FNPs coach their mentees through various nursing tasks, such as performing physical exams, prescribing medications and interpreting laboratory results. Their teaching extends beyond textbook knowledge as they also share valuable insights based on their experience, combining theoretical learning with practical application.
In addition, FNPs play an essential part in shaping young nurses’ ethical and professional conduct, teaching them compassion, patient empathy and effective communication — three vital skills required for a fulfilling nursing career.
FNPs’ contributions to shaping future nursing professionals
Becoming a family nurse practitioner involves more than mere medical competence; it calls for a holistic approach combining medical knowledge, interpersonal skills and in-depth knowledge of community health. FNPs act as mentors and help nursing students strike this balance.
They foster a culture of lifelong learning by instilling curiosity and an avid appetite for knowledge in their students. They also encourage them to stay abreast of healthcare developments to continually improve nursing practice.Through their mentorship, FNPs also assist students in building strong leadership and critical thinking abilities, equipping them for any challenges and motivating them towards excellence in their careers.
Effect of FNP mentorship on patient care and nursing practice
Mentorship of FNPs has an immense effect on patient care and general nursing practice. Mentoring allows students to provide high-quality services by learning from and adopting best practices from their mentors. By sharing real-life experiences, FNPs give students a more in-depth knowledge of medical situations. In addition, FNPs teach them to personalize care plans to meet diverse patient needs.
FNP mentoring also enhances healthcare collaboration as students gain experience working within multi-disciplinary teams, which helps improve their adaptability and cooperative skills for more streamlined patient care.
Mentoring also influences nursing practice by encouraging evidence-based care. FNP mentors promote using research findings as the basis of nursing decisions, which helps to improve patient outcomes and drive innovation in healthcare delivery.
Conclusion
Family nurse practitioners are multifaceted healthcare professionals. They manage multiple roles, providing essential patient care. FNPs make an extraordinary contribution to healthcare. Their comprehensive care improves patient outcomes, reduces hospitalizations and enhances patient satisfaction. Through advocacy and education, they support healthier communities and better-informed patients, while their contributions to research and policy help inform practice improvements for up-to-date care.
As healthcare evolves, so will the role of FNPs. Technological advances, changing patient demographics and changes to healthcare policy will all influence their future roles. Yet, one thing is certain — FNPs will remain at the heart of patient care, advocating for their patients while furthering the nursing profession.